DynO: Dynamic Onloading of Deep Neural Networks from Cloud to Device
Recently, there has been an explosive growth of mobile and embedded applications using convolutional neural networks(CNNs). To alleviate their excessive computational demands, developers have traditionally resorted to cloud offloading, inducing high infrastructure costs and a strong dependence on networking conditions. On the other end, the emergence of powerful SoCs is gradually enabling on-device execution. Nonetheless, low- and mid-tier platforms still struggle to run state-of-the-art CNNs sufficiently. In this paper, we present DynO, a distributed inference framework that combines the best of both worlds to address several challenges, such as device heterogeneity, varying bandwidth and multi-objective requirements. Key components that enable this are its novel CNN-specific data packing method, which exploits the variability of precision needs in different parts of the CNN when onloading computation, and its novel scheduler that jointly tunes the partition point and transferred data precision at run time to adapt inference to its execution environment. Quantitative evaluation shows that DynO outperforms the current state-of-the-art, improving throughput by over an order of magnitude over device-only execution and up to 7.9x over competing CNN offloading systems, with up to 60x less data transferred.
Authors: M. Almeida*,S. Laskaridis*, S. I. Venieris*, I. Leontiadis*, N. D. Lane
Published at: ACM Transactions of Embedded Computing Systems (TECS’22), Special Issue on Accelerating AI on the Edge
Overview
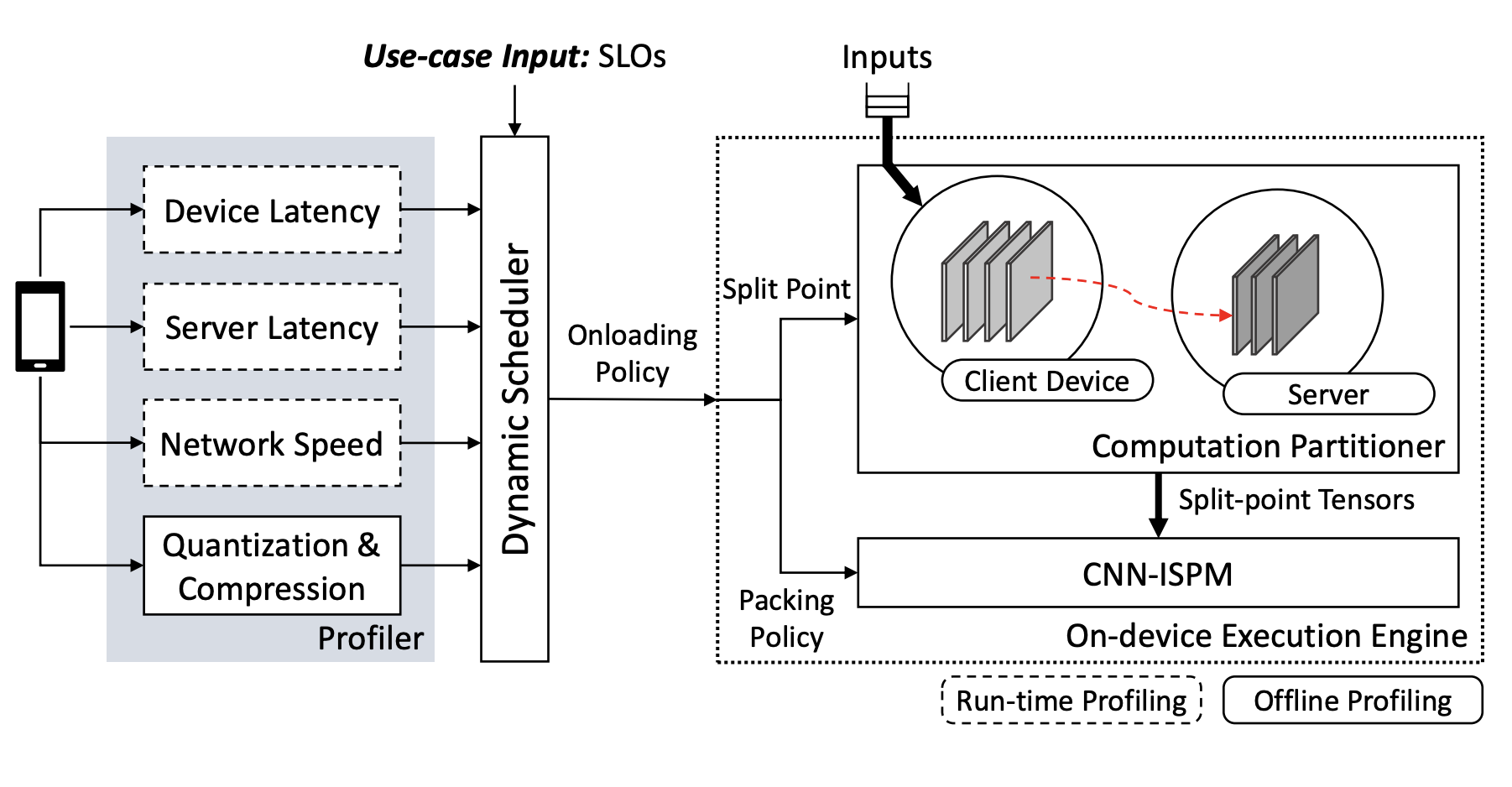
In DynO, we explored how to dynamically split inference between device and cloud under changing network and hardware conditions. We combined CNN-aware data packing, which exploits varying precision sensitivity across layers, with a runtime scheduler that jointly selects partition points and transmission precision.
DynO achieves major throughput improvements over device-only and prior offloading systems, while drastically reducing the amount of data transferred. This work demonstrates how adaptive precision and partitioning can unlock efficient collaborative inference.
Links
Reference
@article{almeida2022dyno,
title={Dyno: Dynamic onloading of deep neural networks from cloud to device},
author={Almeida, Mario and Laskaridis, Stefanos and Venieris, Stylianos I and Leontiadis, Ilias and Lane, Nicholas D},
journal={ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems},
volume={21},
number={6},
pages={1--24},
year={2022},
publisher={ACM New York, NY}
}
